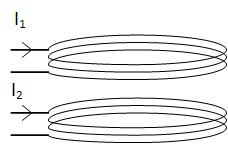
Will the force between them be:
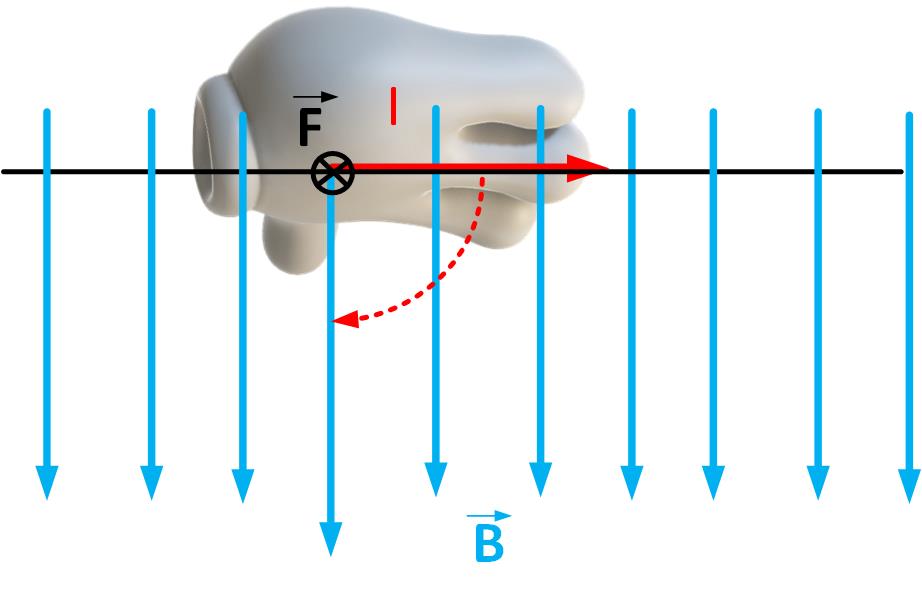
Force on a conductor due to external magnetic field
Force on a conductor of length due to an external magnetic field is
Vector is in the direction of the current. To find the force’s direction, we apply the right-hand rule shown in Figure fig:forceCurrent. We place the current vector in the palm of our right hand, then orient the palm so that the fingers can sweep towards the magnetic field vector.Direction of a magnetic field of a conductor
The direction of a magnetic field of a conductor can be determined using the right-hand rule. If you point the thumb of your right hand in the direction of the current in a straight conductor, your fingers will curl in the direction of the magnetic field.
Observe how the magnetic field changes around a straight conductor. Change the strength and the direction of the current in the applet below. The distance between the magnetic field rings represents the strength of the magnetic field. When the rings are closer, the magnetic field is stronger, and vice versa. The vertical arrow represents the direction of the current. The small horizontal arrow shows the direction of the magnetic field.
Force between two conductors
When a conductor of length , carrying current , is in the vicinity of another conductor , carrying current , the force acts between them.
Where is the force on conductor is the magnetic field due to current in conductor , and is the magnetic field due to current .
To find the direction of the force, you have to use the right-hand rule. Here is a simulation that shows the force when the currents are in the same direction. What is the direction of the force?
This video shows a simulation that shows the force when the currents are in the opposite direction. What is the direction of the force now?
Magnetic field of a loop of current
The right-hand rule can be used to determine the magnetic field’s direction from a loop of current. Point the thumb in the direction of the current, and fingers will curl in the direction of the magnetic field. See the video below that shows a simulation of magnetic field lines around straight and circular conductors.
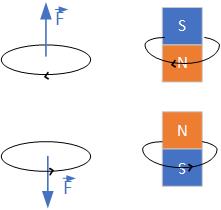
Bar magnet and a loop of current
Permanent magnets have similar magnetic fields to loops of current. The source of the magnetic field of a permanent bar magnet is at the north pole, and the sink is at the south pole. The current loop magnetic field is similar to a bar magnet. The magnetic field lines circulate around the loop. The force between two current loops can be visualized by looking at two permanent magnets. The north pole of a magnet points in the direction of the loop’s magnetic field, as shown in Figure fig:CoupledCoils. We determine the force by looking at the repulsive or attractive force of two bar magnets. We can again see that the force between two loops with currents in the opposite directions is repulsive.