An electron moves with a constant speed in vacuum in a presence of a magnetic field with flux density . The magnetic field can change
Cross product
Cross product is defined as
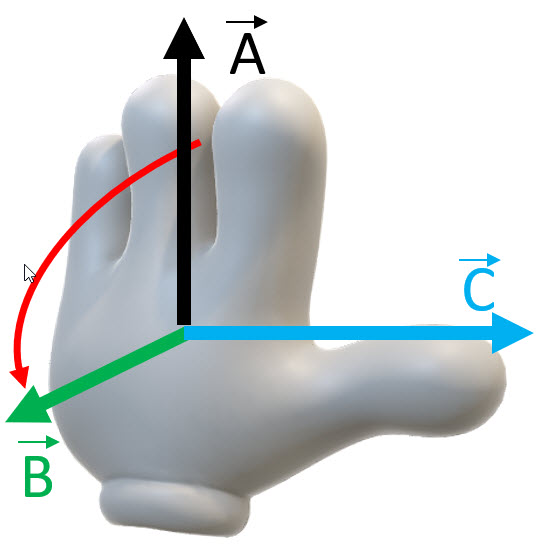
To find the direction of the vector , use the right-hand rule.
- (a)
- Place the first vector in the cross product in the palm of your right hand, and the second vector sticking out perpendicularly to your palm.
- (b)
- Sweep the fingers from vector to and your thumb will be pointing to the direction of the vector .
Magnetic Force on a charged particle
Magnetic force on a charged particle will change the direction of the particle’s path, perpendicularly to the direction of the magnetic field and the velocity vector. However, it will not change the speed of the particle. The magnetic field cannot accelerate a charged particle.
Use the applet below to change the charge, mass, and initial velocity of the particle to see how the path of the particle changes. Note that the initial velocity of the particle is in the horizontal direction.
Lorenz Force
The force on a charged particle in an electric and magnetic field, a Lorentz force, is
is the charge of the particle, is the external electric field, is the particle’s velocity, and is the magnetic field.
Here is an interesting applet that lets you see the charged particle’s path by setting the electric and magnetic fields’ strength, charge and mass of the particle, and the speed direction and magnitude.